Paper
Responsible Hydropower Development in India
Challenges for the Future
Nirmalya Choudhury, Arunabha Ghosh
December 2013 | Sustainable Water
Suggested citation: Choudhury, Nirmalya and Arunabha Ghosh. 2013. Responsible Hydropower Development in India: Challenges for future.. New Delhi: Council on Energy, Environment and Water.
Overview
This paper highlights that hydropower will remain as an important source for electricity in India. It emphasises that responsible hydropower development will ensure a more stable and sustainable investment in the sector over the medium-to-long-term. It provides various methods for leveraging the existing regulations for responsible hydropower development. This paper also identifies two key priorities: going beyond Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) to EIA follow-up and increasing public involvement in decision-making through better processes, which go beyond public hearings.
Key findings
- Hydropower contributes 18 per cent to the total electricity generation in India.
- 97 per cent of the hydropower generation companies are from the public sector. However, the existing plan envisages that the private sector will emerge as one of the leading participants in hydropower development.
- One of the reasons for the private sector’s resurgence in interest in hydropower development is that it is less carbon intensive than thermal power.
- Responsible hydropower development has to ensure that the fragile environmental systems within which the projects are constructed are taken care of. It should also ensure that the social systems that project affect are taken on board to minimise opposition.
- By establishing Environmental Management Systems within the organisation and compliance with standards, a project proponent might voluntarily undertake some EIA follow-up activities.
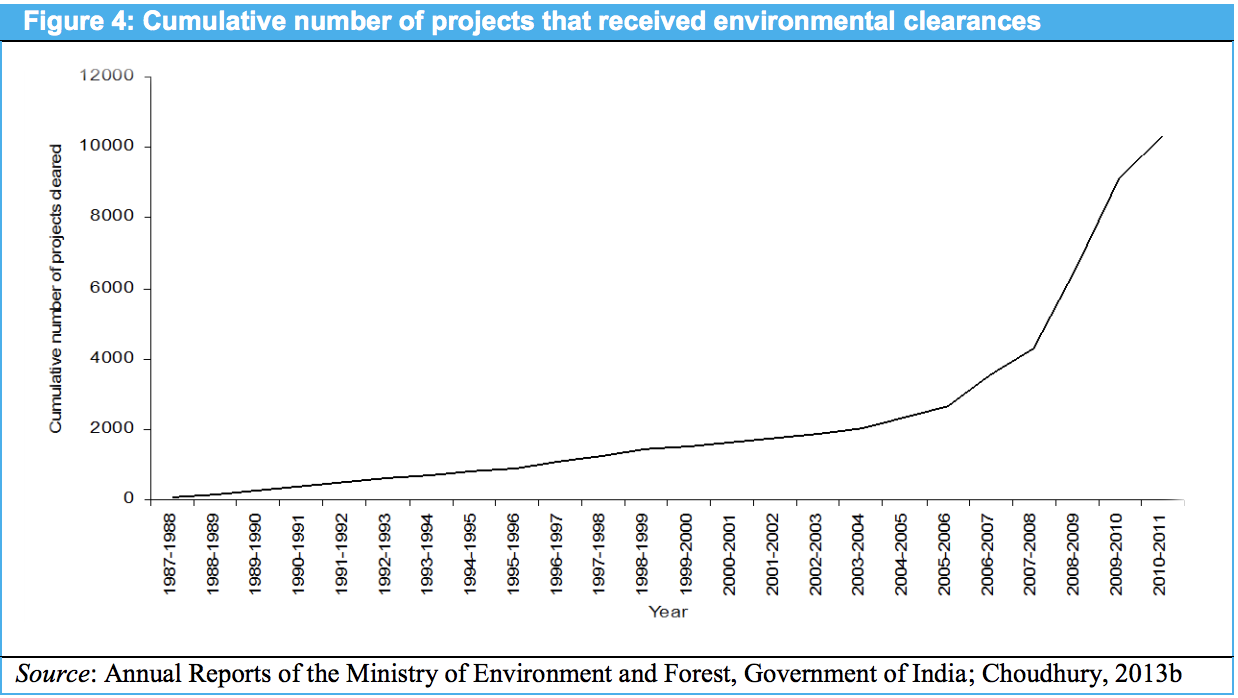
- While the coverage of EIA increased consistently, the number of projects subjected to compliance-monitoring decreased.
- Public involvement during project planning is important as it helps to secure information about the local populace and how they would be affected, address immediate problems and legitimise decisions.
- In India, social impact assessment for a hydropower project is still at the nascent stage and the only institutionalised form of involving the public is during public hearings.
- Public hearing is a component that takes place quite late within the environmental decision-making process.
Key recommendations
- Promote responsible hydropower development through policy initiatives and by encouraging private investment.
- Increase the installed hydropower capacity in the country amongst various existing sectors.
- Make the project affected populace the first beneficiaries of a project. Besides, the project should be able to improve their livelihoods.
- Emphasise on the importance of social impact assessments and the process of undertaking social impact assessment should be participatory and transparent.
- Public involvement should be made an integral part of the screening and scoping phase of environmental clearance procedures.
Public involvement during project planning is important as it helps to secure information about the local populace and how they would be affected, address immediate problems and legitimise decisions.








