Issue Brief
State of Electricity Access for Primary Healthcare Centres in India
Insights from the District Level Household and Facility Survey (DLHS-3 and DLHS-4)
Sunil Mani, Sasmita Patnaik
February 2019 | Energy Transitions, Power Markets
Suggested Citation: Mani, Sunil, Sasmita Patnaik, and Hem H. Dholakia. 2019. State of Electricity Access for Primary Health Centres in India. New Delhi: Council on Energy, Environment and Water.
Overview
This issue brief examines electricity access across Primary Healthcare Centres (PHCs) in India, especially the duration and quality of electricity supply, using data from District Level Household and Facility Survey (DLHS) 3 and DLHS-4. It also elaborates on the existing gaps in the data and design of health systems, and suggests alternatives that could be considered to strengthen electricity access for healthcare facilities to meet the ever-growing need of the population.
Access to electricity in healthcare facilities is key to the efficacy of health service delivery. It is needed for deliveries, storage of vaccines, provision of emergency services, the supply of clean water, as well as retention of skilled staff. One in every two PHCs in India, were either un-electrified or suffered from irregular power supply in 2012-2013.
Key Findings
- A lack of electricity can significantly limit the diagnostic capabilities and treatment services in PHCs. Unavailability of regular electricity supply in the PHCs also has an adverse impact on the availability of the medical staff in the facility.
- In 2012-13, a total of 91 per cent of PHCs had access to electricity, an improvement from 87 per cent in 2007-08.
- Even though 91 per cent of PHCs had electricity connections in 2012-2013, almost half of them had irregular power supply, impeding their ability to provide quality care.
Access to regular electricity supply at PHCs in India has improved between 2007-08 and 2012-13
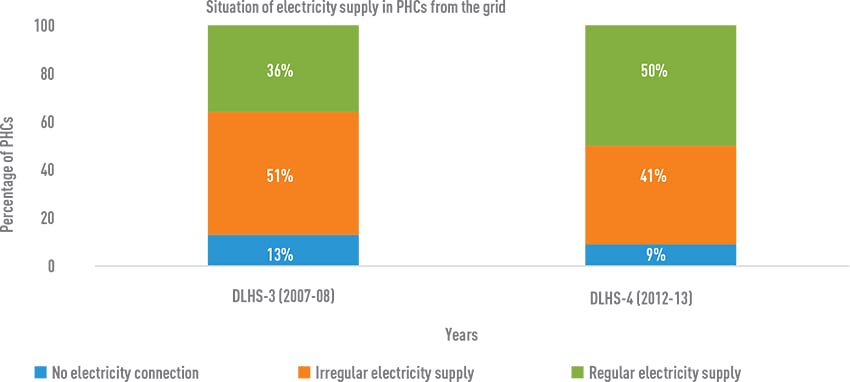
Source: CEEW analysis; DLHS-3 and DLHS-4
- While in Kerala, 93 per cent of all PHCs received regular electricity, in Manipur only eight per cent of all PHCs had access to regular electricity supply. Further, access to reliable electricity varied even within a state.
- In 11 of the 29 states, the number of PHCs with access to regular electricity supply were below the national average of 50 per cent. These 11 states include Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Haryana, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Manipur, Nagaland, Odisha, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
- Eighty-one per cent of PHCs with regular electricity access provided delivery services, while only 33 per cent of PHCs with no electricity connection were able to provide the same.
- While both electricity supply from the grid and the availability of electricity backup in the PHCs has improved over the years, our analysis shows that electricity backup systems are installed at a much higher rate in PHCs that already have electricity supply from the grid.
Service provision improves with improvement in electrification status of the PHCs
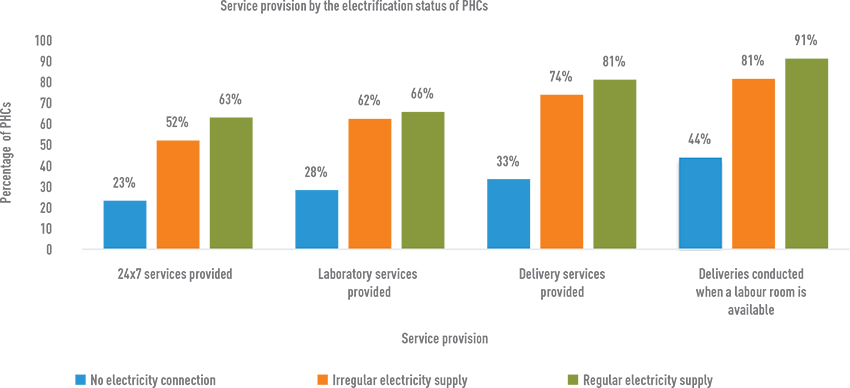
Source: CEEW analysis; DLHS-3 and DLHS-4
Key Recommendations
- Leverage technology to collect better data on the status of electricity available. Integrate more energy indicators into routine annual health facility infrastructure surveys.
- Prioritise PHCs with irregular or no electricity supply for installation of backup.
- Design renewable energy systems to augment the grid. With lesser operational and maintenance costs and greater reliability, renewable energy has the potential to meet the energy requirements of healthcare centres.
- Develop guidelines around the optimal solar system sizes to meet the needs of each PHC.
Access to electricity in healthcare facilities is an important factor of the efficacy of health service delivery. Even though 91 per cent of PHCs in India had electricity connections in 2012-2013, almost half of them had irregular power supply.







