



Suggested Citation: Dholakia, Hem H. and Abhishek Jain. 2015. Lead Acid Battery Recycling in India: Challenges and Next Steps. New Delhi: Council on Energy, Environment and Water.
This issue brief highlights the challenges associated with recycling lead acid batteries in India. It uses existing literature and preliminary primary research through stakeholder interviews to identify the key issues associated with Used Lead Acid Batteries (ULABs) recycling. Further, it recommends the next steps to improve battery recycling through policy action based on sound research.

Today, with our increasing reliance on technology, our need for rechargeable batteries is also on the rise. From handheld gadgets to automotive sector and household inverters, rechargeable batteries are ubiquitous. Except few applications including small batteries for electronic gadgets, most of the rechargeable batteries we use are lead-acid based. Lead acid batteries find a huge and ever rising demand in automotive sector, followed by household inverters and decentralized electrification systems. In India alone, the number of vehicles has increased from 55 million in 2001 to 159.5 million in 2012 (MoRTH, 2013), consequently increasing the demand for lead acid batteries. In India, the lead acid battery market is currently growing at a rate of 16.5% (Technavio, 2014).
Lead, a highly valued metal and themaincomponent of lead acid batteries, is known to be toxic to human health (Chatham-Stephens et al., 2013; Roberts et al., 1974; Steenland & Boffetta, 2000). Case-control studies in India find that workers in battery factories have >10 times blood lead levels as compared to healthy age-matched controls (Rao, Shetty, & Sudha, 2007). In addition to being an occupational hazard to workers, the population at large may also be at risk due to environmental contamination at manufacturing or recycling stages. In a study across India, Indonesia and Philippines, it was estimated that lead exposure (from toxic waste sites) was responsible for a disease burden comparable to that of Malaria and Outdoor Air Pollution (Chatham-Stephens et al., 2013). Children are at the high risk of diminished intelligence due to lead exposure from contaminated soil and water.
As a consequence, handling of lead batteries across the entire valuechain i.e. from manufacturing to recycling has implications for potential exposure and toxicity. Governments the world over have adopted policy frameworks to stem exposure to the toxic metal and protect public health.In most developed and developing countries, such policy is governed by the ‘Extended Producers Responsibility (EPR)’ framework.The over-arching idea of EPR is that responsibility for ‘End of Life’ environmental impacts rest with the original producers and sellers of lead acid batteries. Although the EPR framework exists in India, it faces considerable challenges in its implementation. In this issue brief, we highlight (i) the challenges associated with and (ii) the next steps to improve, the recycling of lead acid batteries in India.
In India, The Batteries Management and Handling Rules (2001) and subsequent 2010 amendment have provided a set of regulations that govern the handling of lead acid batteries (MoEF, 2001). Under these rules, a Deposit Refund System (DRS) is in place for recycling of Lead batteries in the market. Used Lead Acid Batteries (ULABs) procured by retailers are to be sold only to registered (formal) recyclers, who in turn are required to use environmentally friendly processes to recycle the lead (Gupt, 2014). In addition, manufacturers and importers are required to be part of the buy-back system. However, the ground realities are at variance to the intended policy framework.
On the basis of existing literature and preliminary primary research through stakeholder interviews, we have identified following key issues associated with ULABs recycling in India:
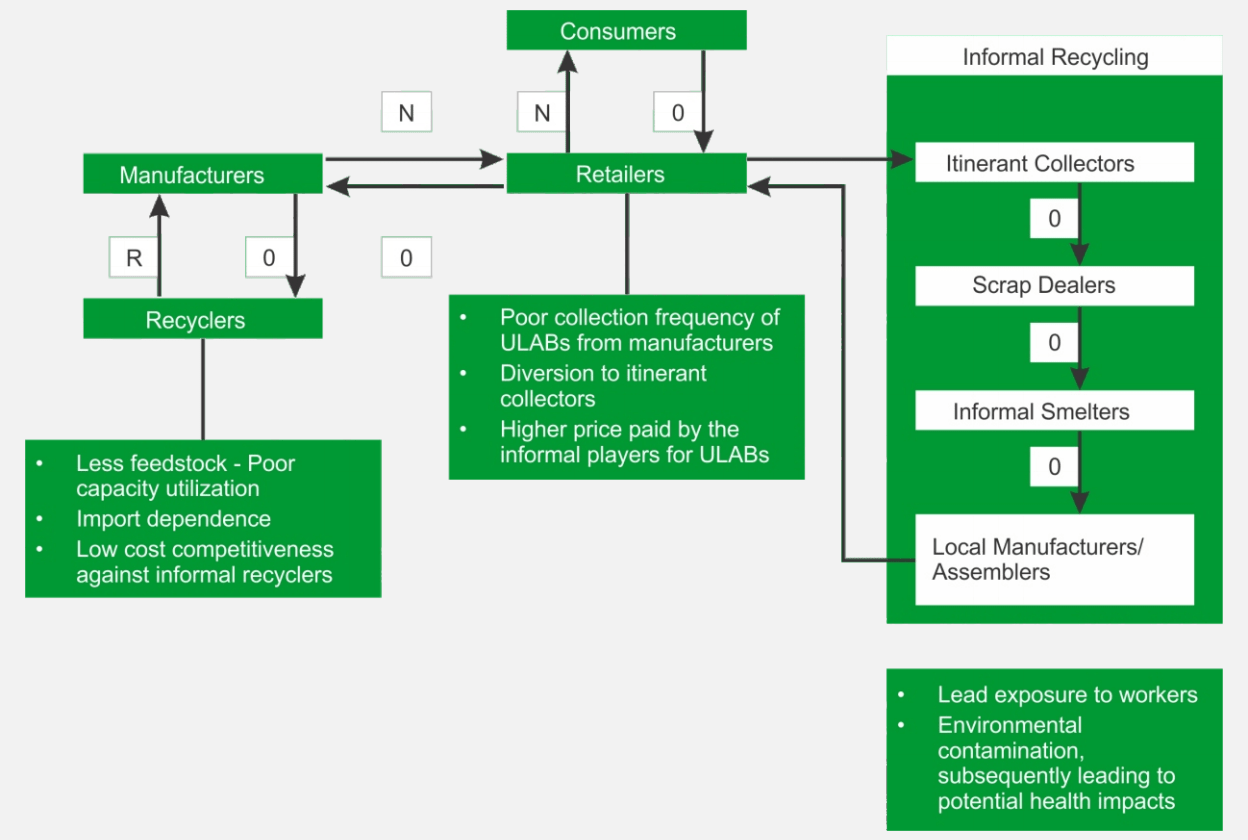
As practically the regulations and associated policing doesnot govern the informal sector, a large number of workers are susceptible to lead exposure. Furthermore, disposal methods are not environment friendly and lead to potential water and soil contamination, posing risk to a larger populations. Figure 1 highlights the current value chain and associated issues (in GREEN boxes).
 Figure 1 - Value chain for Lead recycling (Adapted from Gupt, 2014) N: New Battery, O: Old battery, R: Re-cycled Lead
Figure 1 - Value chain for Lead recycling (Adapted from Gupt, 2014) N: New Battery, O: Old battery, R: Re-cycled Lead
A number of recommendations have been made in the past, in order to remedy the existing challenges associated with informal recycling of lead. These include economic instruments such as ‘Green Tax’ and policy mechanisms such as establishing separate collection agency to improve collection efficiency and frequency of formal recyclers/ manufacturers (Gupt, 2014). Each of these measures aims to increase efficiency of the value chain for formal recyclers and to potentially eliminate informal recycling.
However, implementing these prescriptions may prove very challenging. This is because there remains heterogeneity across geographies with respect to the extent of informal recycling and economic incentives that drive them.
As a consequence, a ‘one size fits all’ approach may prove ineffective. In India, The data required for sound and implementable policy amendments (e.g. proportion of market share of formal vs. informal recycling, processes used by informal smelters, price differentials between formal and informal systems, number of workers exposed etc.) remain scanty.
A detailed analysis of these issues will help develop more targeted policies. Even if informal recycling system cannot be stamped out in the short run, understanding the processes where human exposure happens and educational interventions for safer environmental practices within the informal system could go a long way to protect human health.
To this end, there is an urgent need to address the current challenges associated with recycling of lead acid batteries in India. This would require not only sound implementable policies, but a greater effort on awareness generation front, in order to curb informal and unsafe recycling practices. Such policies and awareness generation programs need to be based on sound, unbiased, scientific research while filling data gaps, detailing the processes and associated exposures across the value chain, and understanding economic and non-economic incentives of involved stakeholders. These policies and programmes when enacted would significantly contribute towards safe-guarding the environment and protecting human health from lead exposure.

Enabling Circular Economy in Used Water Management in India

Toolkit for "Preparing City Action Plans for Reuse of Treated Used Water"

Activating Circular Economy for Sustainable Cooling

Activating Circular Economy for Sustainable Cooling

Activating Circular Economy for Sustainable Cooling