This report, in collaboration with the SELCO Foundation and supported by the Good Energies Foundation, analyses the financiers’ perspective in lending for solar-powered livelihood appliances in India. It generates evidence on the impact of solar-powered productive-use technologies on the net incomes of end-users and their loan repayments. This helps financiers understand the economic viability of these technologies. It also assesses the prevailing policy solutions and provides recommendations for the private sector, policymakers and donors to improve access to finance for end-users of such products.
The findings are based on interviews with bankers at the state and national level, civil society organisations and other financiers. To understand the economic viability of solar-powered livelihood appliances, the report also analyses the data on income, revenue, cash flow and loan repayment of 300 micro enterprises for two specific technologies supported by SELCO Foundation – sewing machines and digital service centres called Lok Seva Kendras (LSKs).
Most tailoring enterprises can recover their investment from solarising their sewing machines in less than two years
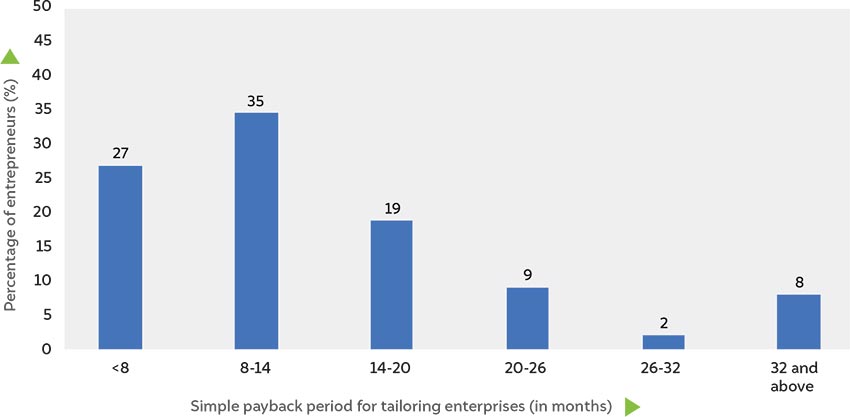
Source: Author's analysis
As much as 61 percent of existing tailoring enterprises and 65 percent of existing LSK enterprises are able to repay the product loan from their increased incomes.







